
Medically Reviewed by Dr. Lee Hwee Chyen
MBBS MRCP (UK) FAMS (Dermatology)
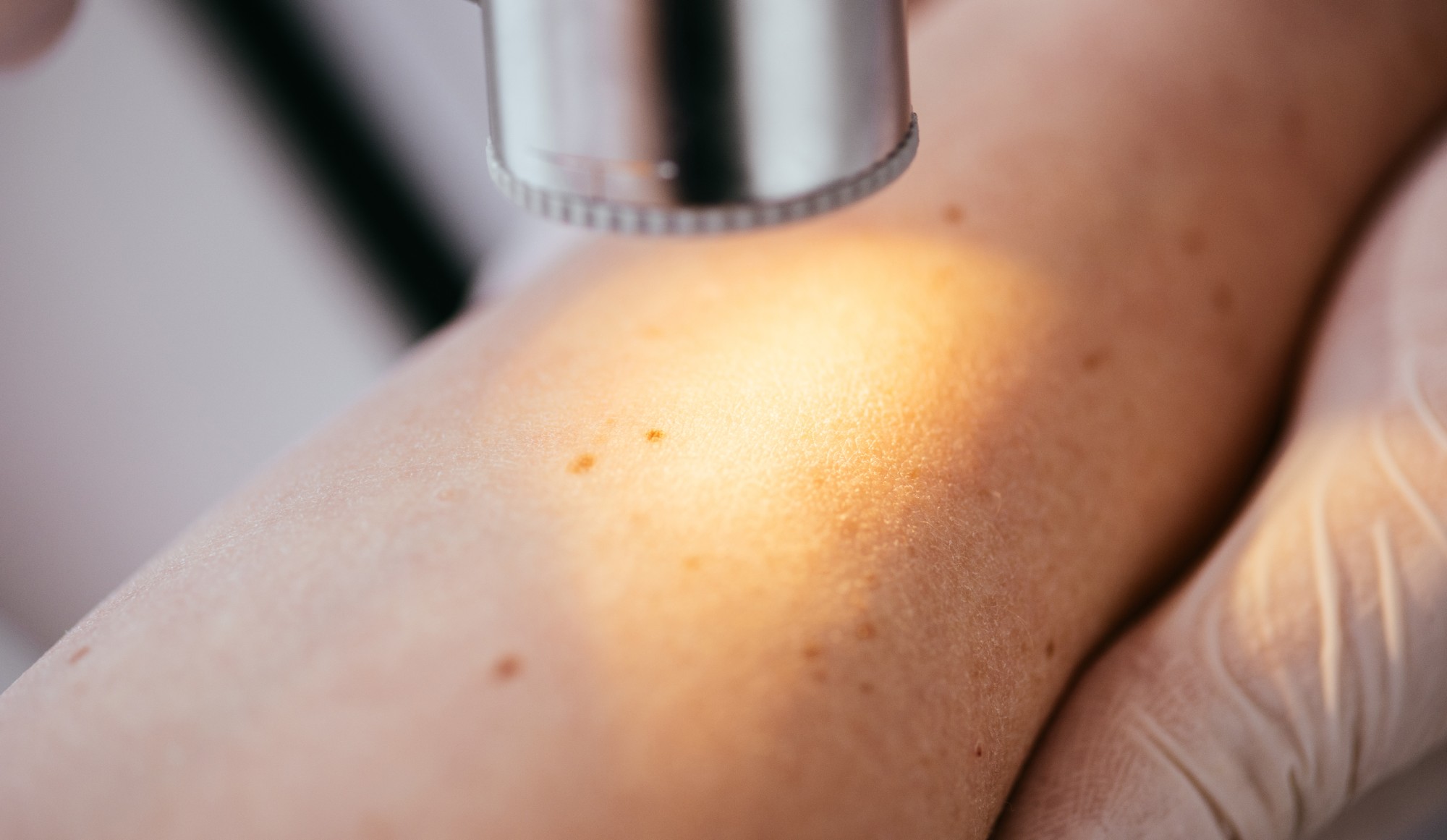
A skin biopsy is a medical procedure in which a small sample of skin tissue is removed for examination under a microscope. Depending on the characteristics of the lesion, different biopsies such as a shave biopsy, punch biopsy, or an excisional biopsy may be carried out.
The primary purpose of a skin biopsy is to diagnose skin conditions accurately when a visual examination of a skin lesion or abnormality is insufficient for a definitive diagnosis.
Before a biopsy, a consultation with the dermatologist is carried out, which may include:
Preparing well for a skin biopsy will ensure the procedure goes smoothly and can reduce the risk of complications.
Avoid applying lotions, creams, or other skin care products to the area where the biopsy will be performed to reduce the risk of infection.
Wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing on the day of the biopsy, especially if the biopsy site is likely to be covered by clothing. Avoid wearing perfume to prevent irritation of the biopsy area post-procedure.
Inform your dermatologist of all medications and supplements taken. Some medications, like blood thinners or certain supplements, may need to be paused under the guidance of your dermatologist to reduce the risk of bleeding.
While skin biopsies are generally safe procedures, they carry potential risks and complications like any medical procedure.
Minor bleeding at the biopsy site is common, especially immediately after the procedure. However, significant bleeding is rare and can usually be controlled with simple pressure and topical treatments.
There is a small risk of infection at the biopsy site, which is minimized by proper wound care and hygiene. Signs of infection include redness, swelling, increased pain, and pus discharge, which require medical attention.
Biopsies may result in some form of scarring, which can be addressed with post-procedural skin care and treatments.
Eczema and psoriasis can be mistaken for one another because of their similar symptoms. Read on to learn more about how they differ in several key aspects that help dermatologists diagnose both conditions distinctively.
A skin biopsy involves the surgical removal of a small sample of skin tissue for microscopic examination, allowing for the identification of diseases that may not be discernible through visual inspection alone. Read on to learn more.
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that originates in the melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its colour. Unlike other skin cancers, melanoma has a higher potential to spread to other parts of the body and become life-threatening if not detected and treated early.