
Medically Reviewed by Dr. Lee Hwee Chyen
MBBS MRCP (UK) FAMS (Dermatology)
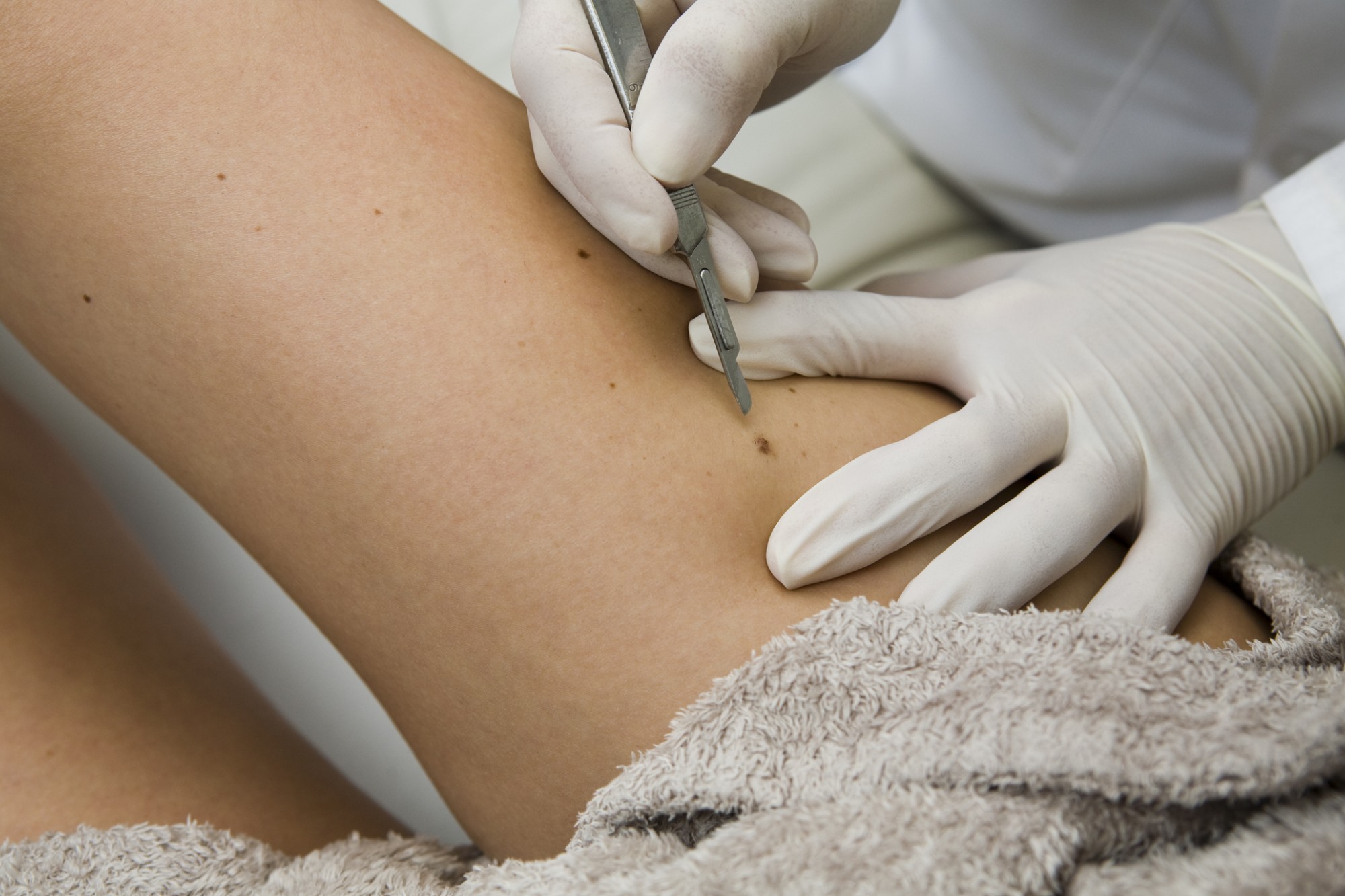
A skin biopsy involves the surgical removal of a small sample of skin tissue for microscopic examination. It allows a range of skin diseases, from benign lesions to malignant tumours, to be diagnosed.
Each type of biopsy is suited for different diagnostic purposes and has its specific applications.
The upper layers of the skin are removed using a surgical blade to diagnose lesions that protrude above the skin surface, such as moles or skin tags. It is less invasive and ideal for diagnosing and removing superficial skin growths.
A circular tool is used to remove a small, round piece of skin, including deeper layers below the skin. This helps diagnose inflammatory skin conditions and small lesions that require a deeper tissue sample.
This involves removing the entire lesion surgically so that it can be removed with a low risk of recurrence and also sent for histological evaluation.
A portion of a large lesion is removed for examination. Sufficient tissue is retrieved to diagnose a possibly malignant lesion that is too large to be completely removed at the initial assessment.
The histological examination of skin tissue samples via a biopsy allows for the identification of diseases that may not be discernible through visual inspection alone.
Conditions such as moles, cysts, and benign growths can be confirmed through biopsy. Benign lesions can be distinguished from malignant ones.
Via microscopic examination, inflammatory skin conditions like psoriasis, eczema, and lupus can be diagnosed. This reveals specific patterns of inflammation and cellular changes characteristic of these diseases.
Skin biopsies can determine the causative organism of infections caused by bacteria, fungi, or viruses and guide appropriate treatment. This includes conditions like cellulitis, fungal infections, and viral warts.
Skin cancers, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma can be diagnosed via skin biopsies. It provides definitive evidence of malignancy, the type of cancer and its extent for staging and treatment planning.
Rare and complex skin disorders like pemphigus, dermatomyositis, and cutaneous lymphomas can be diagnosed using skin biopsies when clinical presentation is insufficient.
Skin biopsies are used by dermatologists for many purposes, including:
Moles are common skin growths, typically appearing as small, dark brown spots and are caused by clusters of pigmented cells. Read on to learn more about mole removal.
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that originates in the melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its colour. Unlike other skin cancers, melanoma has a higher potential to spread to other parts of the body and become life-threatening if not detected and treated early.
Addressing common misconceptions about acne can help you adopt the best practices for an acne-free and healthy skin environment. Consult a dermatologist if you have any concerns about your skin condition and for medication to treat severe acne.