
Medically Reviewed by Dr. Lee Hwee Chyen
MBBS MRCP (UK) FAMS (Dermatology)
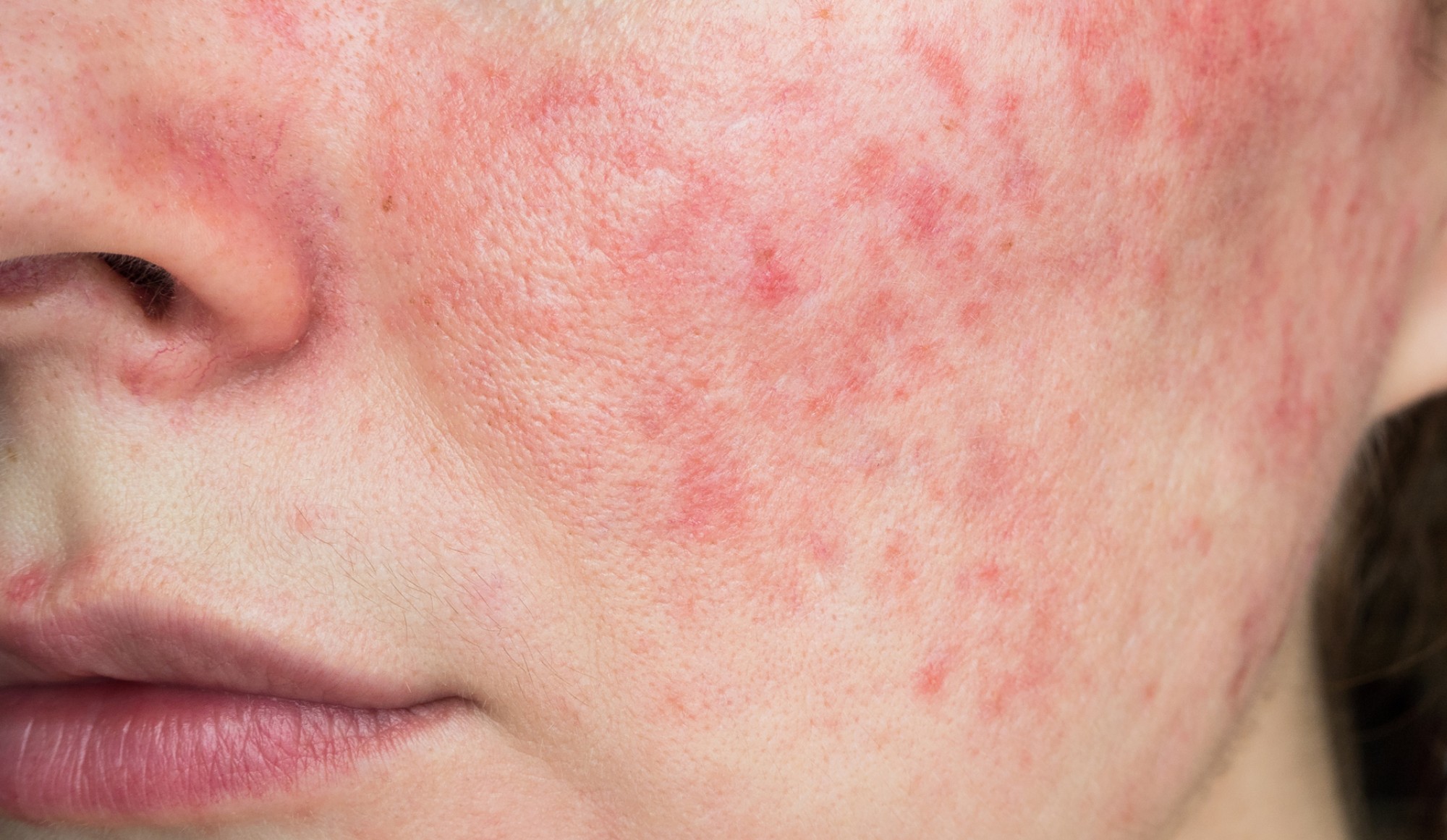
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition characterized by facial redness, swelling, and sometimes acne-like bumps. It primarily affects the central face, including the cheeks, nose, chin, and forehead. Although rosacea can occur in anyone, it is most commonly seen in middle-aged women, particularly during menopause.
Menopause, the cessation of menstrual cycles, typically occurs in women between the ages of 45 and 55. It is a natural biological process accompanied by various physiological changes due to fluctuating hormone levels, especially a decrease in oestrogen.
Hormonal changes during menopause can exacerbate or trigger the onset of rosacea in some women due to the sudden reduction in oestrogen and progesterone production by the ovaries. These hormonal changes can lead to hot flushes, night sweats, sleep disturbances, and mood swings.
Rosacea and menopause are primarily linked to the decline in oestrogen during menopause, which helps manage skin health. Menopause-associated symptoms such as hot flushes and increased stress levels may also influence the development of rosacea.
The decrease in oestrogen during menopause leads to a reduction in skin thickness, hydration, and elasticity, making the skin more prone to redness and irritation. As oestrogen levels drop, the skin becomes thinner and less able to retain moisture, leading to increased dryness, redness and irritation associated with rosacea.
Menopause-related hormonal imbalances can heighten the skin’s sensitivity, making it more reactive to external stimuli. This increased sensitivity means that environmental factors such as sunlight, extreme temperatures, and certain skincare products can more easily trigger rosacea flare-ups.
Hot flushes, a common symptom of menopause, can trigger rosacea symptoms due to the dilation of blood vessels in the skin. This leads to an increase in skin redness and flushing, characteristic of rosacea.
The emotional and psychological stresses of menopause, including mood swings and increased stress levels, can also exacerbate rosacea. Elevated stress can also lead to higher levels of cortisol, a hormone that promotes inflammation.
As hormonal changes during this period can aggravate rosacea symptoms, a combination of topical and oral medications, skin care practices, and approaches to stabilise stress and hormone levels are needed.
Topical medication helps alleviate swelling, reduce redness and manage symptoms of rosacea such as rashes. Oral antibiotics may also be prescribed due to their anti-inflammatory properties and antibacterial effects.
These therapies target visible blood vessels and reduce redness, a key symptom of rosacea. During laser therapy, wavelengths of light are emitted and absorbed by the red pigment in blood vessels. This helps to diminish the appearance of these vessels and reduces overall redness.
Light therapy, including IPL (Intense Pulsed Light), treats the broader skin area to improve skin texture and tone, which can be especially affected by menopause. Because menopausal skin can be more sensitive, consult with a dermatologist before embarking on laser or light therapy.
Use gentle, non-abrasive cleansers to prevent exacerbation of rosacea as menopausal skin is more prone to irritation. Avoid products with harsh chemicals or exfoliants which can irritate the skin. Opt for fragrance-free, hypoallergenic cleansers to minimize the risk of rosacea flare-ups.
Cleanse with lukewarm water, as hot water can trigger rosacea symptoms. Pat the skin dry gently instead of rubbing it to avoid aggravating the skin.
Moisturise the skin regularly as menopause can cause dryness and worsen rosacea symptoms. Look for products with hyaluronic acid and/or ceramides to enhance the skin’s moisture barrier and alleviate the dry skin associated with menopause.
Apply moisturiser while the skin is still damp to lock in hydration. Use oil-free and non-comedogenic moisturizers to avoid clogging pores, which can otherwise cause swelling of the skin. Night-time moisturizing is especially beneficial to repair and hydrate skin overnight.
Wear sunscreen daily as ultraviolet ray exposure from the sun can trigger rosacea flare-ups. Choose sunscreens designed for sensitive skin to avoid irritation. Physical sunscreens with zinc oxide or titanium dioxide are often better tolerated by rosacea-prone skin that is especially sensitive during menopause. Wear hats and seek shade for additional protection.
Ingredients like niacinamide or green tea extract can help reduce swelling and redness in menopausal skin and strengthen the skin barrier. Anti-inflammatory ingredients can also offer relief during rosacea flareups, and help maintain a calmer, more balanced skin condition.
Use serums or creams containing these ingredients as part of your daily skincare routine.
During menopause, the skin becomes more sensitive, making it more reactive to common irritants. Avoid skincare products containing alcohol as they can dry out and irritate the skin, leading to rosacea flare-ups.
Witch hazel and fragrance should also be avoided as these ingredients can cause irritation and inflammation in sensitive skin, worsening rosacea symptoms.
Often found in ‘cooling’ products, menthol can trigger redness and flushing in rosacea-prone skin and should be avoided.
Activities like yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels and alleviate the symptoms of menopause that can aggravate rosacea.
Engaging in regular physical activity can balance hormones and reduce stress. A balanced diet rich in antioxidants and omega-3 fatty acids supports hormonal health and overall health.
Laser therapy is a minimally invasive treatment that uses concentrated light to address various skin conditions. Here are five skin conditions that you can treat with the help of laser therapy.
By understanding the role of nutrition in skin health and including certain nutrient-rich foods in one's diet, individuals can support their skin's health from the inside out.
Topical Vitamin C serum can serve as a valuable addition to a skincare regimen, particularly in acne management. Read on to learn more about the benefits of topical Vitamin C serum for the skin and acne.