
Medically Reviewed by Dr. Lee Hwee Chyen
MBBS MRCP (UK) FAMS (Dermatology)
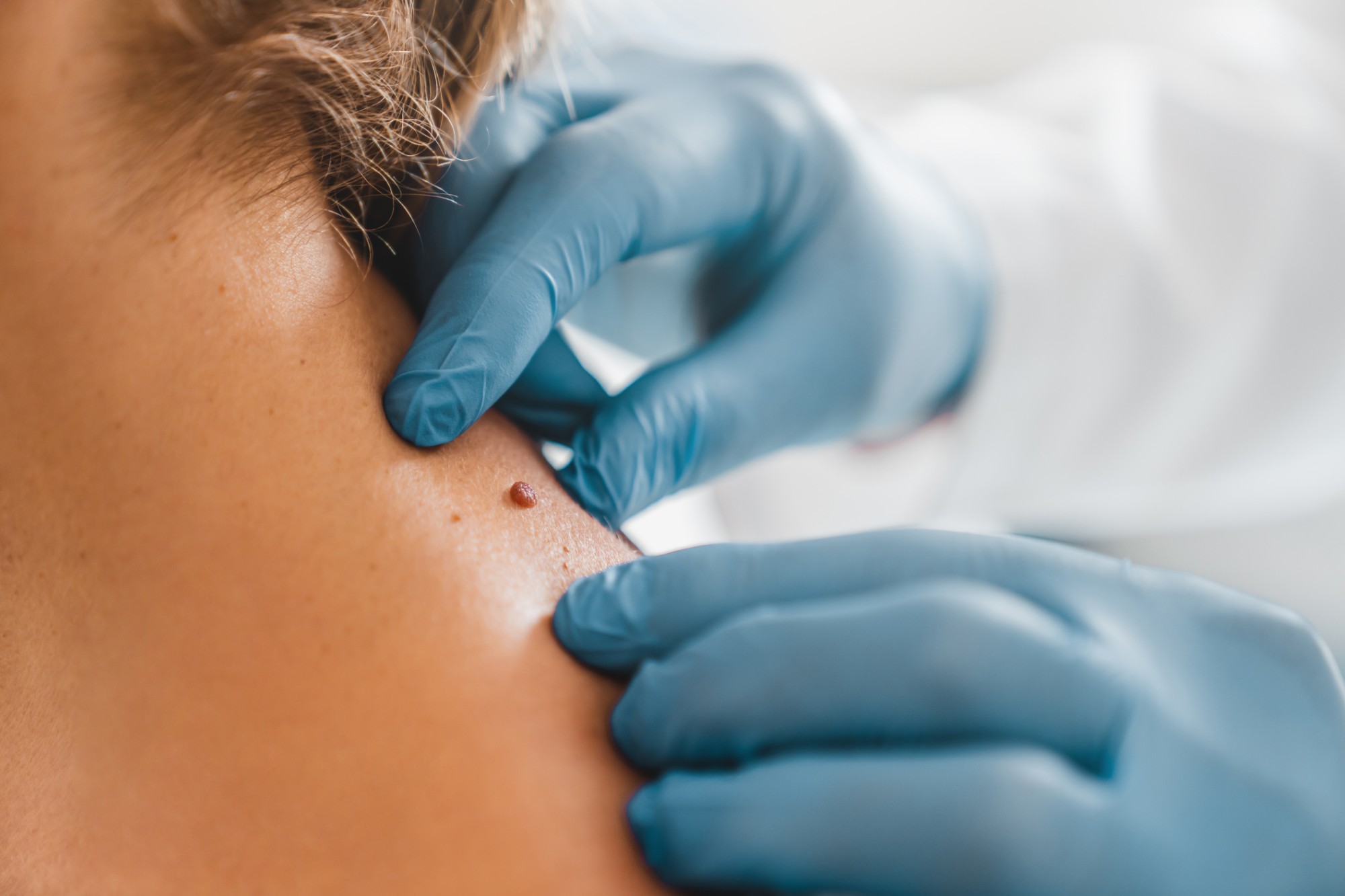
Moles are common skin growths. They typically appear as small, dark brown spots and are caused by clusters of pigmented cells. They may be flat or raised. Although usually harmless and often requiring no treatment, moles may develop into melanoma, a serious form of skin cancer, in some cases.
The following are key indicators that a mole should be evaluated by a dermatologist who specialises in skin cancer detection, and potentially removed:
There are various surgical techniques used by dermatologists to remove moles, each suited for different types of moles. Your dermatologist will assess the mole and decide which method of removal is most suitable depending on the type/nature of mole, and if there are any features suspicious for malignancy.
Involves cutting out the entire mole along with a margin of surrounding healthy skin, followed by suturing the site. Typically used for larger or potentially cancerous moles.
This method involves numbing the area and shaving raised moles down to the level of the surrounding skin. Stitches are not generally required.
Utilised for smaller, flat, benign moles, this method uses concentrated light beams to break down the mole cells. It may require multiple sessions.
Although mole removal is generally a safe procedure, there still are potential risks and considerations:
Atypical moles have irregular shapes, uneven colouring, or other unusual characteristics. They can sometimes be precursors to melanoma, a potentially life-threatening form of skin cancer. When removed, the risk of developing melanoma from atypical moles is reduced.
Moles that are raised or located in areas where they are prone to rubbing against clothing can cause discomfort. Removal of these moles prevents repeated irritation or trauma to a mole, which can lead to inflammation or even infection.
Moles in hidden areas like the underarms or groin can hinder personal hygiene practices. Their removal facilitates easier cleaning and grooming, contributing to better overall skin care and hygiene.
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that originates in the melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its colour. Unlike other skin cancers, melanoma has a higher potential to spread to other parts of the body and become life-threatening if not detected and treated early.
Addressing common misconceptions about acne can help you adopt the best practices for an acne-free and healthy skin environment. Consult a dermatologist if you have any concerns about your skin condition and for medication to treat severe acne.
By understanding the role of nutrition in skin health and including certain nutrient-rich foods in one's diet, individuals can support their skin's health from the inside out.