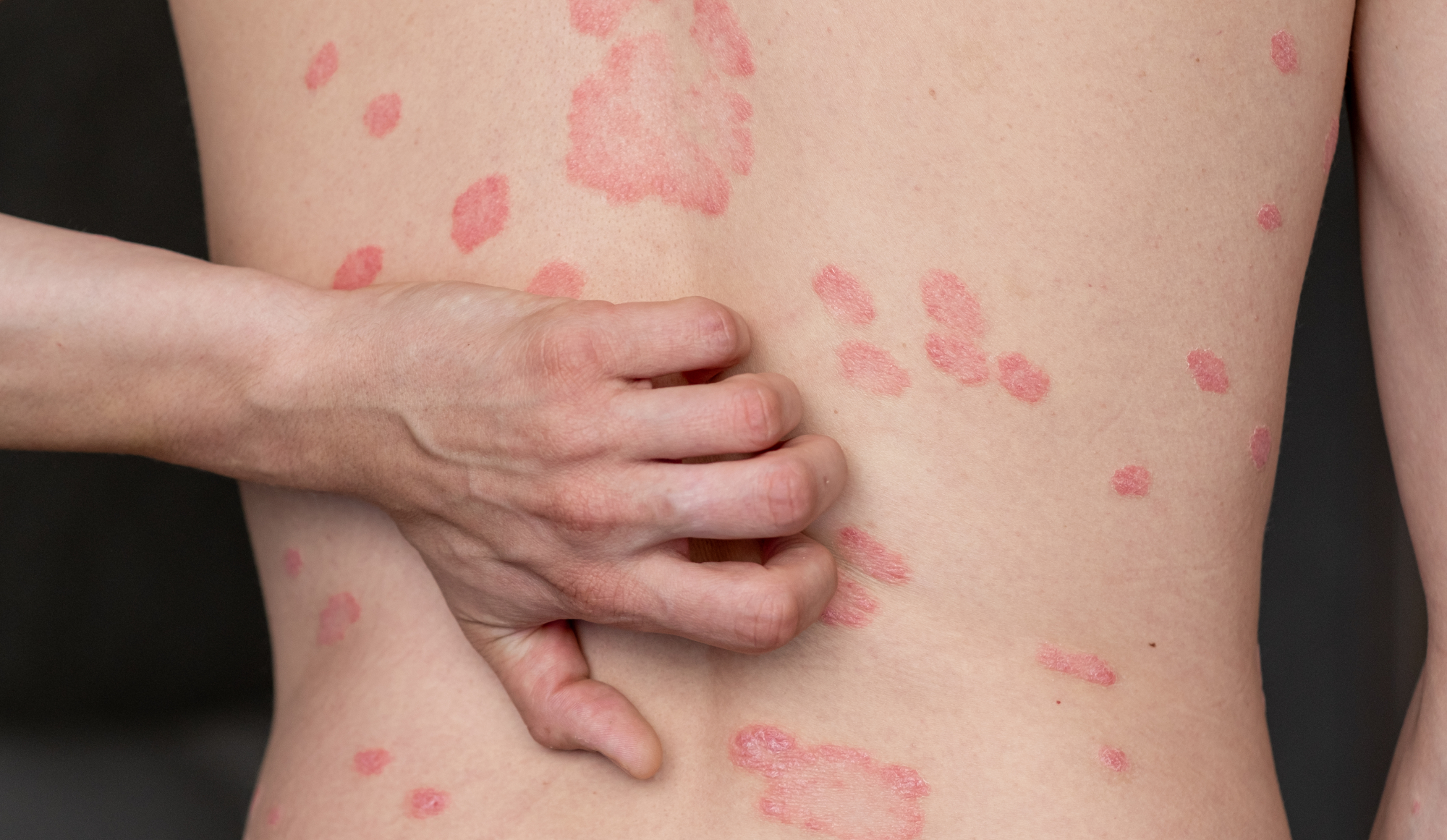
What is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that accelerates the life cycle of skin cells, causing them to build up rapidly on the skin’s surface. This buildup results in bumpy red patches covered with white scales, which can be itchy and sometimes painful. While the exact cause is unknown, it’s believed to involve the immune system, genetics, and environmental factors.
Psoriasis affects both genders equally and can appear at any age, with its severity varying widely among individuals. Although there’s no cure, treatment can manage symptoms effectively.
Does Age Affect Psoriasis?
Age can influence the onset, progression, and severity of psoriasis. While psoriasis can develop at any age, its appearance and the challenges associated with managing the condition can vary across different life stages. Understanding how psoriasis affects individuals at various ages is crucial for providing age-appropriate care and support.
Psoriasis Across Different Age Groups
Childhood and Adolescent Psoriasis
- Often presents unique diagnostic and management challenges.
- Early onset is sometimes linked to a stronger family history.
- Severity can vary significantly.
- Treatment approaches aim to minimize side effects while managing symptoms effectively.
Adult-Onset Psoriasis
- The majority of cases are diagnosed in adulthood.
- Can be triggered by stress, skin injury, and certain medications.
- Symptoms and plaque locations include scalp, knees, elbows, and torso.
- Experiences a wider range of symptoms and locations.
Psoriasis in Older Adults
- Management includes considerations for other chronic conditions.
- Careful use of treatments due to age-related changes in skin and health.
- Increased sensitivity to side effects from systemic treatments.
- More frequent monitoring is required.
Management of Psoriasis
Effective management of psoriasis requires a personalized approach, taking into account the patient’s age, health status, and lifestyle.
Multiple treatment options for psoriasis are available, and the choice of treatment depends on the severity and extent of the condition.
These include:
- Topical Therapies: Including corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, retinoids and coal tar, for mild to moderate psoriasis.
- Phototherapy: Light therapy for widespread psoriasis or when topical treatment isn’t effective.
- Systemic Medications: Such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, and acitretin for more severe cases.
- Biologics: Targeted therapies for moderate to severe psoriasis, including TNF-alpha inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors, and IL-23 inhibitors.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Stress reduction techniques, a balanced diet, and avoiding triggers like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Treatment Considerations for Children
In children, the focus is on gentle, safe treatments that minimize side effects. Topical therapies are preferred. More extensive cases of psoriasis can opt for phototherapy which is a relatively safe and effective treatment option for children and adolescents who can cooperate with the treatment process. For severe cases, systemic treatments are used cautiously and risks/side effects versus benefits must be discussed with the parent or guardian.
Treatment Considerations for adults
Adult treatment strategies might include a broader range of options, tailored to the severity and impact of the disease. Aside from topicals, phototherapy and systemic medications (oral immunosuppressants and injectable biologics), lifestyle modifications need to be reinforced for adults. Avoidance of triggers such as stress, smoking and excessive alcohol should be reinforced. Regular exercise and a healthy well balanced diet also facilitates improvement.
Special Considerations for adults and systemic associations
Research has shown that psoriasis has a strong association with multiple co-morbidities. Patients with psoriasis are predisposed to a higher risk of health conditions that are more common with older age groups.
These include:
- Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease
– Older patients with psoriasis have been found to have a higher risk of developing high cholesterol, high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, fatty liver disease. These metabolic conditions, along with age, increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. This is why lifestyle modifications as mentioned above are crucial to older patients with psoriasis.
- Depression
– There is strong evidence that demonstrates psoriasis is linked with depression. Patients with psoriasis, especially older patients, are strongly encouraged to seek psychosocial support along with medical treatment for psoriasis. It is thus important to adopt a multidisciplinary approach in the management of psoriasis, especially in that of older patients who are more prone to psychosocial problems.
- Osteoporosis
– Studies have also suggested that patients with psoriasis for a longer duration have an increased risk of developing osteoporosis. Early prevention is crucial and patients with psoriasis should be encouraged to maintain adequate levels of calcium and vitamin D (through lifestyle and diet) as well as to perform weight-bearing exercises when young.
Special considerations for older adults with psoriasis
For older adults, managing other chronic conditions and minimizing medication side effects are priorities. Treatments may need adjustment due to changes in skin sensitivity and the presence of other health conditions.
- Gentle Topical Treatments: Due to increased skin sensitivity in older adults. Topical steroids should also be used with caution as older adults may be more prone to skin thinning and atrophy.
- Careful Use of Systemic Treatments: Monitoring for potential interactions with medications for other health conditions.
- Regular Health Monitoring: For potential comorbidities associated with psoriasis and its treatments.
Conclusion
Psoriasis management requires a multidisciplinary approach that considers the patient’s age, life stage, and unique health profile. Recognizing how age-related factors influence psoriasis can guide the selection of appropriate treatments and support strategies, aiming for the best possible quality of life at any age.